Forms of MS at diagnosis
Course of the disease
Primary Progressive MS (PPMS)
PPMS is a debilitating form of the disease marked by steadily worsening symptoms, typically without distinct relapses or periods of remission. However, some people with PPMS do experience relapses. PPMS tends to be more disabling than RRMS. The accumulation of irreversible disability is twice as high in PPMS than in RRMS, which can mean people with PPMS rely more on mobility aids or wheelchairs.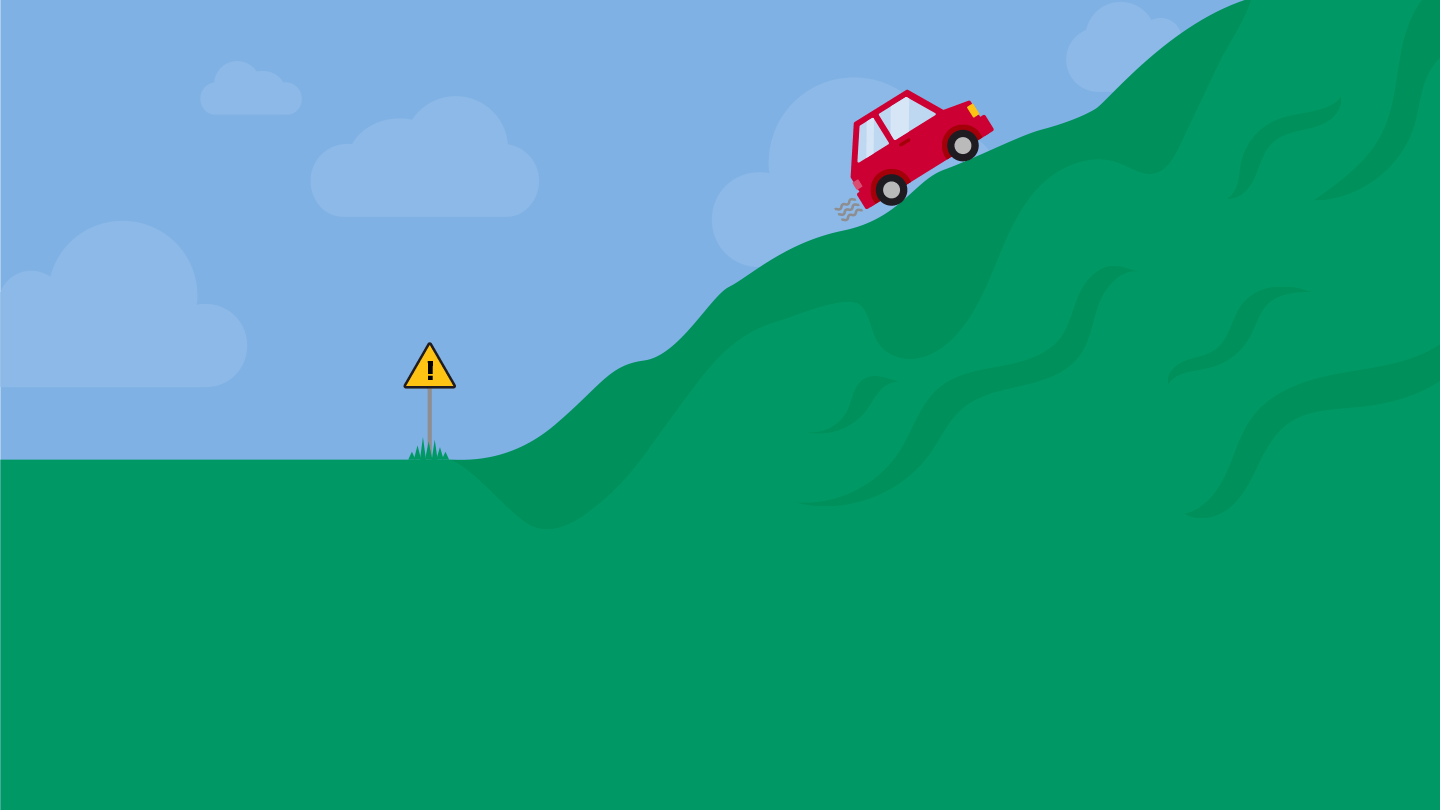
Symptoms
Primary Progressive MS (PPMS)
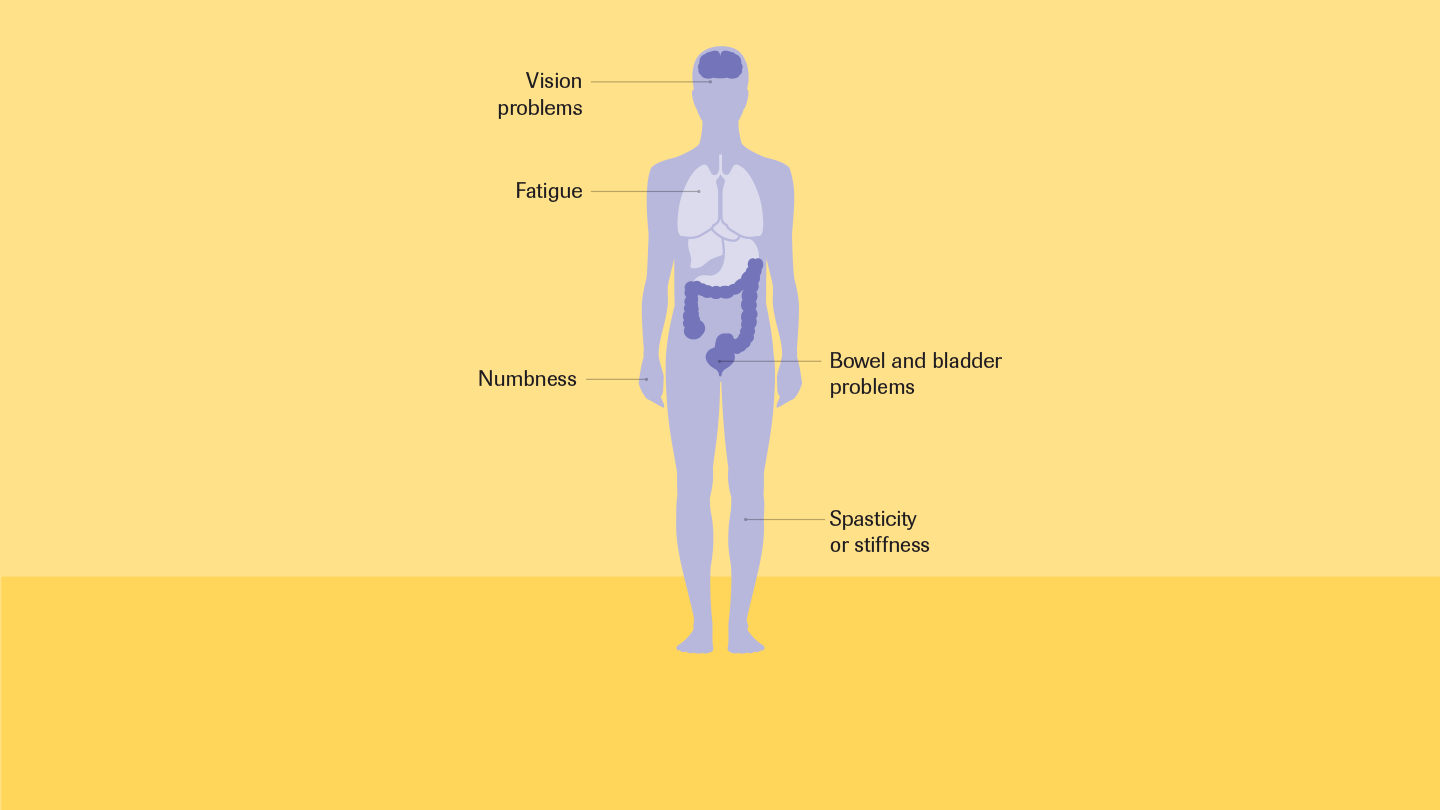
The most commons symptoms in PPMS include progressive weakness, mobility issues and spasticity. These symptoms are not unique to PPMS but tend to be more persistent and difficult to manage. People may also have more problems thinking and speaking compared to people with RRMS.
Age at diagnosis
Ratio of men and women diagnosed
Disease activity
Unmet clinical need
Primary Progressive MS (PPMS)
PPMS is a highly disabling disease, therefore treatment should be based on clinical need and initiated as early as possible.Recent advances in the scientific understanding of MS have resulted in the development of new treatments that may slow disease progression in PPMS. There are no approved disease-modifying treatments for people with PPMS in many countries around the world, including Europe.